This JupyterLab notebook provides a step-by-step symbolic solution using SymPy for the 3-phase parallel RLC circuit in the Extra Credit Problem. The circuit is a three - phase circuit and has per phase:
AC source:
The source is connected with parallel comnination of R (), L ( reactance), C (100 MVA total rating).
We have the following circuit conditions: Pre-switching: steady-state. For this state, we will compute the initial conditions using phasor analysis.
Post-switching (S opens at ): For the state when the switch opens at the source current equal to 0A, we have free parallel RLC oscillations.
We will plot and to visualize each waveform.
Imports and Setup¶
import sympy as sp
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sympy import I, Abs, sqrt, exp, cos, sin, symbols, re, pi, arg
sp.init_printing(use_unicode=True)Analysis Steps¶
Step 1: Derive Circuit Parameters¶
In this step, we symbolically define the given parameters and derive the per-phase capacitance , inductance , and capacitive reactance . The source is line-to-line RMS voltage kV at rad/s. Capacitor rating is 100 MVA (3-phase), inductor , resistor .
Per phase: , MVA, , , .
omega = symbols(r'\omega', real=True, positive=True)
R = symbols('R', real=True, positive=True)
XL = symbols('X_L', real=True, positive=True)
XC = symbols('X_C', real=True, positive=True)
V_llrms = symbols('V_llrms', real=True, positive=True)
Q_c3ph = symbols('Q_c3ph', real=True, positive=True)
L = XL / omega
C = 1 / (omega * XC)RMS Phase Voltage¶
V_ph_rms = V_llrms / sp.sqrt(3)
V_ph_rmsPer Phase Capacitor Reactive Power Capacity¶
Q_cph = Q_c3ph / 3
Q_cphCapacitive Reactance Equation¶
Xc_eq = (V_ph_rms)**2 / Q_cph
Xc_eqInductance Equation¶
L_eq = XL / omega
L_eqCapacitance Equation¶
C_eq = 1 / (omega * Xc_eq)
C_eqSubstitute Values to Calculate Capacitive Reactance¶
numerical_subs = {omega: 377, R: 1, XL: 1, V_llrms: 10e3*sp.sqrt(3), Q_c3ph: 100*10**6}
numerical_subscalc_Xc = Xc_eq.subs(numerical_subs).doit().evalf()
calc_XcDisplay Results of Calculating Inductance, Capacitance and Capacitive Reactance¶
display(sp.Eq(sp.symbols('C'), C_eq)) # Symbolic expression
C_num = C_eq.subs(numerical_subs).doit().evalf()
print(f"Numerical C = {C_num:.2e} F ({C_num*1e6:.0f} μF)")
L_num = L_eq.subs(numerical_subs).doit().evalf()
print(f"Numerical L = {L_num:.2e} H")
Xc_num = Xc_eq.subs(numerical_subs).doit().evalf()
print(f"Numerical X_C = {Xc_num:.2f} Ω")Numerical C = 8.84e-4 F (884 μF)
Numerical L = 2.65e-3 H
Numerical X_C = 3.00 Ω
Output (Symbolic):
Step 2: Steady-State Analysis (Pre-Switching Phasors)¶
Steady-state ():
Admittances:
Switch at :
Adjust phase:
Therefore:
and:
Inductive Impedance¶
Z_L = sp.I * XL
Z_LInductive Admittance¶
Y_L = 1 / Z_L
Y_LResistive Admittance¶
Y_R = 1 / R
Y_RCapacitive Admittance¶
Y_C = 1 / (-I * XC)
Y_CTotal Admittance¶
Y_total = Y_R + Y_L + Y_C
Y_totalCalculate Total RMS Load Current¶
I_total_rms = V_ph_rms * Y_total
I_total_rmsCalculate Load Phase Angle¶
angle_Y = sp.arg(Y_total)
angle_YCorrect Phase Angle for Switch Closing at Source Current = 0A¶
theta = pi / 2 - angle_Y
thetaPhase Voltage in Phasor Form¶
V_ph_adjusted = V_ph_rms * exp(I * theta)
V_ph_adjustedMagnitude of Phase Voltage¶
v0_sym = sqrt(2) * sp.re(V_ph_adjusted)
v0_symCalculate RMS Inductor Current¶
I_L_rms = V_ph_adjusted / Z_L
I_L_rmsi_L0_sym = sp.sqrt(2) * sp.re(I_L_rms)
i_L0_sym# Symbolic
display(sp.Eq(symbols(r'\angle\;Y_{total}'), angle_Y))
display(sp.Eq(symbols(r'\theta'), theta))# Numerical
subs_num = numerical_subs.copy()
subs_num# Restate Xc in ohms
Xc_numsubs_num.update({XC: Xc_num})
subs_numSubstitute into and Evaluate¶
v0_symv0_num = float(v0_sym.subs(subs_num).doit().evalf())
v0_numi_L0_num = float(i_L0_sym.subs(subs_num).doit().evalf())
i_L0_numPhase Angle of Load Impedances in :¶
angle_Y_num = float(angle_Y.subs(subs_num).doit().evalf() * 180 / sp.pi)
angle_Y_numPhase of Voltage in :¶
theta_num = float(theta.subs(subs_num).doit().evalf() * 180 / sp.pi)
theta_numTotal Load Current in :¶
I_total_mag = float(Abs(I_total_rms.subs(subs_num)).doit().evalf())
I_total_magprint(f"Numerical |I_total|_rms = {I_total_mag:.0f} A")
print(f"angle(Y_total) = {angle_Y_num:.2f} deg")
print(f"theta_V = {theta_num:.2f} deg")
print(f"v_C(0+) = {v0_num:.0f} V")
print(f"i_L(0+) = {i_L0_num:.0f} A")Numerical |I_total|_rms = 12019 A
angle(Y_total) = -33.69 deg
theta_V = 123.69 deg
v_C(0+) = -7845 V
i_L(0+) = 11767 A
Output (Symbolic):
Numerical Values:
Step 3: Initial Conditions at ¶
dv0_num = (- v0_num / 1 - i_L0_num) / C_num
print(f"v_C(0+) = {v0_num:.0f} V")
print(f"i_L(0+) = {i_L0_num:.0f} A")
print(f"dv_C/dt(0+) = {dv0_num:.2e} V/s")v_C(0+) = -7845 V
i_L(0+) = 11767 A
dv_C/dt(0+) = -4.44e+6 V/s
Output:
Step 4: Time-Domain Differential Equations¶
Post-switching: Parallel RLC, voltage common.
KCL:
Differentiate KCL:
Differential Equation:
Characteristic Equation:
Define:
t = symbols('t', real=True)
L_for_de = symbols('L', real=True, positive=True)
C_for_de = symbols('C', real=True, positive=True)
v = sp.Function('v')(t)
eq_diff_v_presub = sp.Eq(sp.diff(v, t, 2) + (1/(R*C_for_de)) * sp.diff(v, t) + (1/(L_for_de*C_for_de)) * v, 0)
display(eq_diff_v_presub)eq_diff_v = sp.Eq(sp.diff(v, t, 2) + (1/(R*C)) * sp.diff(v, t) + (1/(L*C)) * v, 0)
display(eq_diff_v)Output (Symbolic):
Step 5: Laplace-Domain Solution¶
s = symbols('s')
I_L0 = symbols('I_{L0}')
V0 = symbols('V_0')
V_s = sp.Function('V')(s)
denom = s**2 + (1/(R*C_for_de))*s + 1/(L_for_de*C_for_de)
dv0_sym = (-V0 / R - I_L0) / C_for_de # From Step 3 symbolic
V_s_sol_for_de = (s * V0 + dv0_sym) / denom
display(sp.Eq(V_s, V_s_sol_for_de))V_s = sp.Function('V')(s)
denom = s**2 + (1/(R*C))*s + 1/(L*C)
dv0_sym = (-V0 / R - I_L0) / C # From Step 3 symbolic
V_s_sol = (s * V0 + dv0_sym) / denom
display(sp.Eq(V_s, V_s_sol))Output (Symbolic):
Simplified:
Step 6: Inverse Laplace Transform (Time-Domain Responses)¶
alpha = 1 / (2 * R * C)
alphaomega0 = 1 / sqrt(L * C)
omega0omegad = sqrt(omega0**2 - alpha**2)
omegadzeta = alpha / omega0
zetaA = V0
AB = (dv0_sym + alpha * V0) / omegad
Bv_standard = exp(-alpha * t) * (A * cos(omegad * t) + B * sin(omegad * t))
v_standardD = I_L0
DE = (V0 / L + alpha * I_L0) / omegad
Ei_L_standard = exp(-alpha * t) * (D * cos(omegad * t) + E * sin(omegad * t))
i_L_standardShow Symbolic Equations¶
display(sp.Eq(sp.Function('v')(t), v_standard))display(sp.Eq(sp.Function('i_L')(t), i_L_standard))Evaluate Numerically¶
subs_num_full = numerical_subs.copy()
subs_num_fullsubs_num_full.update({R:1, XL:1, XC:Xc_num, V0:v0_num, I_L0:i_L0_num, C:C_num, L:L_num})
subs_num_fullalpha_num = float(alpha.subs(subs_num_full).doit().evalf())
alpha_numomega0_num = float(omega0.subs(subs_num_full).doit().evalf())
omega0_numomegad_num = float(omegad.subs(subs_num_full).doit().evalf())
omegad_numzeta_num = float(zeta.subs(subs_num_full).doit().evalf())
zeta_numA_num = v0_num
A_numB_num = (dv0_num + alpha_num * v0_num) / omegad_num
B_numD_num = i_L0_num
D_numE_num = (v0_num / L_num + alpha_num * i_L0_num) / omegad_num
E_numprint(f'$5$')$5$
print(f"alpha = {alpha_num:.1f} [rad/s]")
print(f"omega_0 = {omega0_num:.1f} [rad/s]")
print(f"zeta = {zeta_num:.3f}")
print(f"omega_d = {omegad_num:.1f} [rad/s]")
print(f"A = {A_num:.0f} [V], B = {B_num:.0f} [V]")
print(f"D = {D_num:.0f} [A], E = {E_num:.0f} [A]")alpha = 565.5 [rad/s]
omega_0 = 653.0 [rad/s]
zeta = 0.866
omega_d = 326.5 [rad/s]
A = -7845 [V], B = -27175 [V]
D = 11767 [A], E = 11323 [A]
Output (Symbolic):
Numerical:
=
=
=
= 0.866
= -7845 , B = -27175
= 11767 , E = 11323
Step 7: Numerical Simulation and Plots¶
Lambdify for evaluation. t=0 to 0.1 s, dt=1 μs. Verify ICs via eval at t=0.
v_func = lambda tt: np.exp(-alpha_num * tt) * (A_num * np.cos(omegad_num * tt) + B_num * np.sin(omegad_num * tt))
v_func<function __main__.<lambda>(tt)>i_L_func = lambda tt: np.exp(-alpha_num * tt) * (D_num * np.cos(omegad_num * tt) + E_num * np.sin(omegad_num * tt))
i_L_func<function __main__.<lambda>(tt)>t_num = np.arange(0, 0.04, 1e-4)v_plot = v_func(t_num)i_L_plot = i_L_func(t_num)Verify Results¶
print(f"v_C(0) = {v_plot[0]:.0f} V (should be {v0_num:.0f} V)")v_C(0) = -7845 V (should be -7845 V)
print(f"i_L(0) = {i_L_plot[0]:.0f} A (should be {i_L0_num:.0f} A)")i_L(0) = 11767 A (should be 11767 A)
dv_plot_0 = np.gradient(v_plot, t_num)[0]
print(f"dv_C/dt(0) ≈ {dv_plot_0:.2e} V/s (should be {dv0_num:.2e} V/s)")dv_C/dt(0) ≈ -4.03e+06 V/s (should be -4.44e+6 V/s)
# Numerical Simulation and Plots
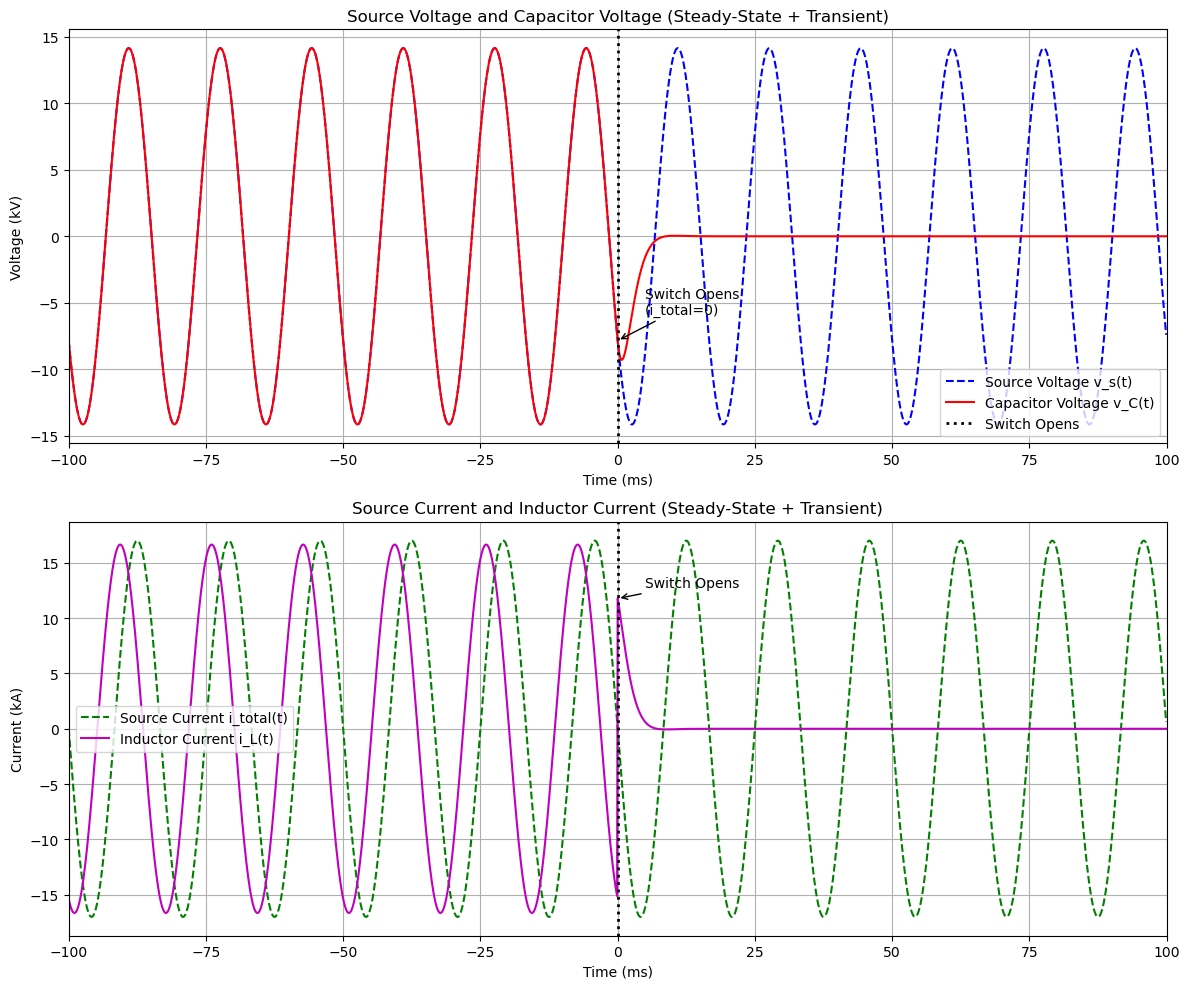
# Extended plots: Steady-state pre-switching (t < 0) and transients post-switching (t >= 0).
# Time: -0.1 to 0.1 s (few cycles before/after), dt=1 μs.
# Steady-state:
# - Source voltage v_s(t) = sqrt(2) V_ph_rms cos(ω t + θ)
# - Source current i_total(t) = sqrt(2) |I_total| cos(ω t + θ + ∠Y_total)
# - Steady-state v_C(t) = v_s(t) (parallel, directly across source)
# - Steady-state i_L(t) = sqrt(2) |I_L_rms| cos(ω t + θ + ∠I_L)
# Annotate t=0 with vertical line "Switch Opens".
# Lambdify transients (post t=0)
v_trans_func = lambda tt: np.exp(-alpha_num * tt) * (A_num * np.cos(omegad_num * tt) + B_num * np.sin(omegad_num * tt))
i_L_trans_func = lambda tt: np.exp(-alpha_num * tt) * (D_num * np.cos(omegad_num * tt) + E_num * np.sin(omegad_num * tt))# Time vector: -0.1 to 0.1 s
t_num = np.arange(-0.1, 0.1, 1e-4)
switch_time = 0 # t=0# Steady-state functions (for t < 0)
V_ph_peak = np.sqrt(2) * 10000
V_ph_peakI_total_peak = np.sqrt(2) * I_total_mag
I_total_peakI_L_peak = np.sqrt(2) * i_L0_num
I_L_peakangle_I_L = float(arg(I_L_rms.subs(subs_num)).doit().evalf() * 180 / pi)
print("Computed angle_I_L = {:.2f} deg".format(angle_I_L))Computed angle_I_L = 33.69 deg
# Numerical omega
omega_num = 377.0
v_s_ss = lambda tt: V_ph_peak * np.cos(omega_num * tt + theta_num * np.pi / 180)
i_total_ss = lambda tt: I_total_peak * np.cos(omega_num * tt + theta_num * np.pi / 180 + angle_Y_num * np.pi / 180)
v_C_ss = v_s_ss # Same as source
i_L_ss = lambda tt: I_L_peak * np.cos(omega_num * tt + theta_num * np.pi / 180 + angle_I_L * np.pi / 180)
# Combined waveforms
v_C_combined = np.where(t_num < switch_time, v_C_ss(t_num), v_trans_func(t_num))
i_L_combined = np.where(t_num < switch_time, i_L_ss(t_num), i_L_trans_func(t_num))
# Verify ICs (continuity at t=0)
idx_switch = np.argmin(np.abs(t_num - switch_time))
print(f"v_C(-) ≈ {v_C_ss(t_num[idx_switch-1]):.0f} V, v_C(0+) = {v_trans_func(t_num[idx_switch]):.0f} V")
print(f"i_L(-) ≈ {i_L_ss(t_num[idx_switch-1]):.0f} A, i_L(0+) = {i_L_trans_func(t_num[idx_switch]):.0f} A")
dv_plot_0 = np.gradient(v_C_combined, t_num)[idx_switch]
print(f"dv_C/dt(0) ≈ {dv_plot_0:.2e} V/s (should be {dv0_num:.2e})")
# Plots: 2 figures - one for voltages (source/v_C), one for currents (source/i_total, i_L)
fig1, (ax1a, ax1b) = plt.subplots(2, 1, figsize=(12, 10))
# Source voltage and v_C
ax1a.plot(t_num * 1000, v_s_ss(t_num) / 1000, 'b--', linewidth=1.5, label='Source Voltage v_s(t)')
ax1a.plot(t_num * 1000, v_C_combined / 1000, 'r-', linewidth=1.5, label='Capacitor Voltage v_C(t)')
ax1a.axvline(x=switch_time * 1000, color='k', linestyle=':', linewidth=2, label='Switch Opens')
ax1a.annotate('Switch Opens\n(i_total=0)', xy=(0, v0_num / 1000), xytext=(5, v0_num / 1000 + 2),
arrowprops=dict(arrowstyle='->', color='black'), fontsize=10)
ax1a.grid(True)
ax1a.set_xlabel('Time (ms)')
ax1a.set_ylabel('Voltage (kV)')
ax1a.set_title('Source Voltage and Capacitor Voltage (Steady-State + Transient)')
ax1a.set_xlim([-100, 100])
ax1a.legend()
# Source current and i_L (steady-state only for i_total, as post-switch no source current)
ax1b.plot(t_num * 1000, i_total_ss(t_num) / 1000, 'g--', linewidth=1.5, label='Source Current i_total(t)')
ax1b.plot(t_num * 1000, i_L_combined / 1000, 'm-', linewidth=1.5, label='Inductor Current i_L(t)')
ax1b.axvline(x=switch_time * 1000, color='k', linestyle=':', linewidth=2)
ax1b.annotate('Switch Opens', xy=(0, i_L0_num / 1000), xytext=(5, i_L0_num / 1000 + 1),
arrowprops=dict(arrowstyle='->', color='black'), fontsize=10)
ax1b.grid(True)
ax1b.set_xlabel('Time (ms)')
ax1b.set_ylabel('Current (kA)')
ax1b.set_title('Source Current and Inductor Current (Steady-State + Transient)')
ax1b.set_xlim([-100, 100])
ax1b.legend()
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
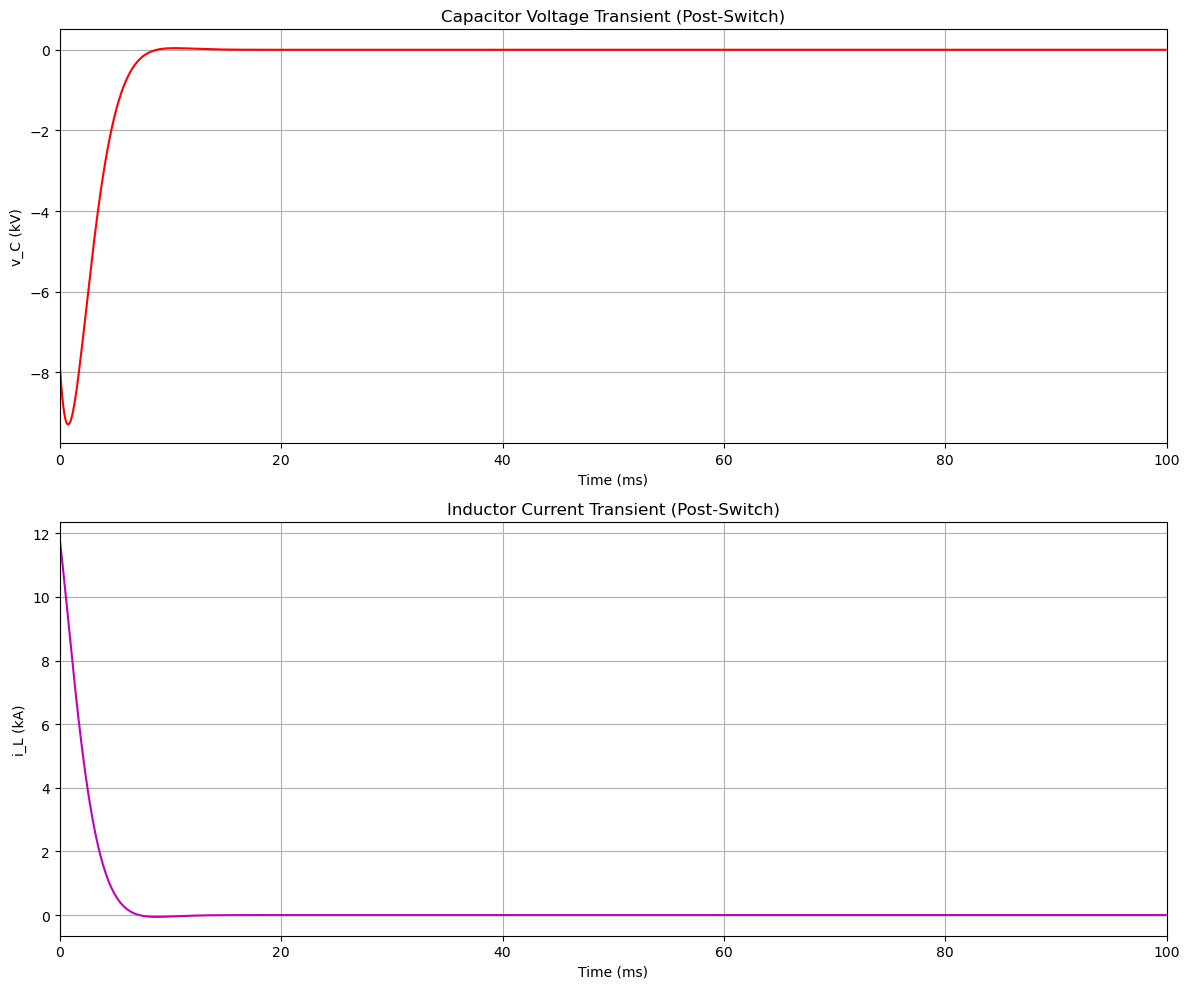
# Additional plot: Zoom on transients post-switch (t=0 to 0.1 s)
fig2, (ax2a, ax2b) = plt.subplots(2, 1, figsize=(12, 10))
ax2a.plot(t_num[t_num >= 0] * 1000, v_C_combined[t_num >= 0] / 1000, 'r-', linewidth=1.5)
ax2a.grid(True)
ax2a.set_xlabel('Time (ms)')
ax2a.set_ylabel('v_C (kV)')
ax2a.set_title('Capacitor Voltage Transient (Post-Switch)')
ax2a.set_xlim([0, 100])
ax2b.plot(t_num[t_num >= 0] * 1000, i_L_combined[t_num >= 0] / 1000, 'm-', linewidth=1.5)
ax2b.grid(True)
ax2b.set_xlabel('Time (ms)')
ax2b.set_ylabel('i_L (kA)')
ax2b.set_title('Inductor Current Transient (Post-Switch)')
ax2b.set_xlim([0, 100])
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()v_C(-) ≈ -7396 V, v_C(0+) = -7845 V
i_L(-) ≈ -15109 A, i_L(0+) = 11767 A
dv_C/dt(0) ≈ -4.26e+06 V/s (should be -4.44e+6)
Compare to Simulation¶
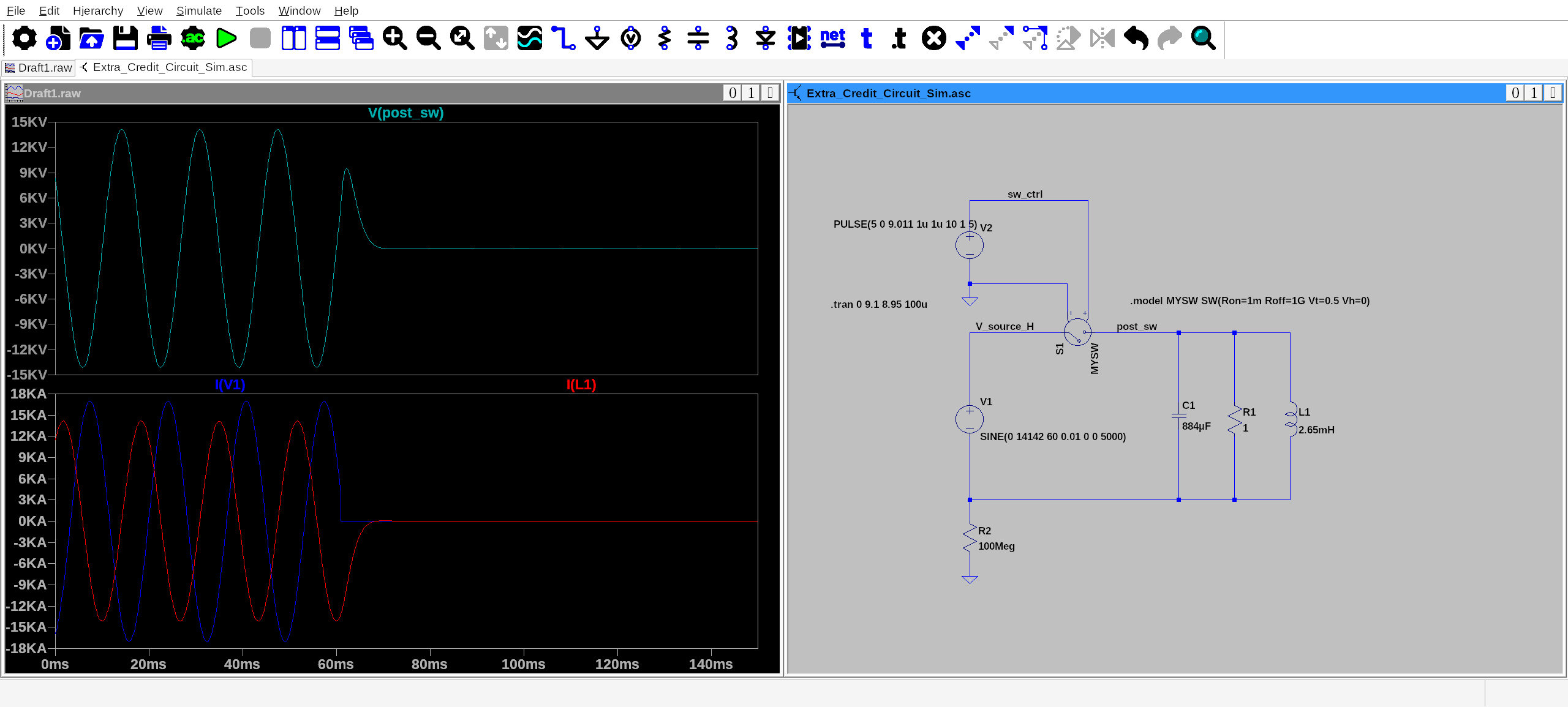
Figure 1:EEE571 Extra Credit Problem Circuit Simulation